Primary vs. Secondary Packaging: What’s The Difference & Which Is Better
Packaging plays a crucial role in the success of a product, ensuring its safe transportation, brand recognition, and consumer appeal. Within the realm of packaging, two distinctive categories exist: primary packaging and secondary packaging. Understanding the differences between these two types is essential for effective product presentation and protection. Let’s delve deeper into primary and secondary packaging and explore their respective roles.

What Is Primary Packaging?
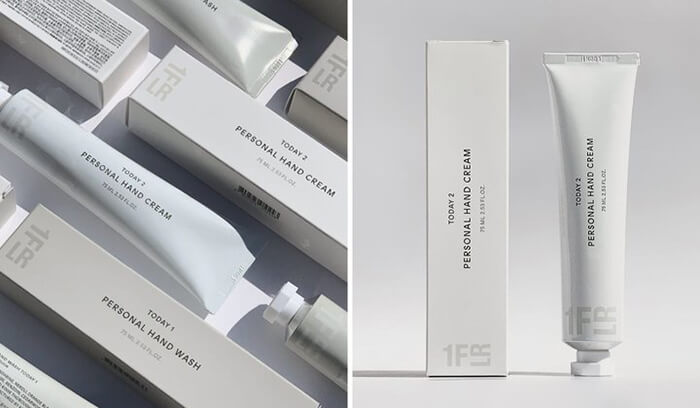
Primary packaging refers to the immediate and direct contact packaging for a product. It is the layer that directly interacts with the product and is typically the most visually prominent to consumers. A primary packaging example for a food item would be the plastic wrap encasing a sandwich or the bottle containing a refreshing beverage. In the realm of cosmetics, primary packaging includes items like mascara tubes, lipstick casings, or perfume bottles. The primary packaging serves several critical functions:
- Product Protection: Primary packaging safeguards the product from external factors, such as moisture, air, light, or contamination, maintaining its quality and integrity.
- Convenience and Usability: Primary packaging ensures ease of use, storage, and application of the product. It often includes convenient features like dispensers, sprayers, or resealable closures.
- Branding and Differentiation: Primary packaging acts as a canvas for brand identity and communication. It features product names, logos, compelling designs, and labeling information to enhance brand recognition and differentiate products in the market.
- Regulatory Compliance: Primary packaging accommodates essential legal and regulatory information, including ingredient lists, nutritional facts, warnings, and usage instructions, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
What Is Secondary Packaging?
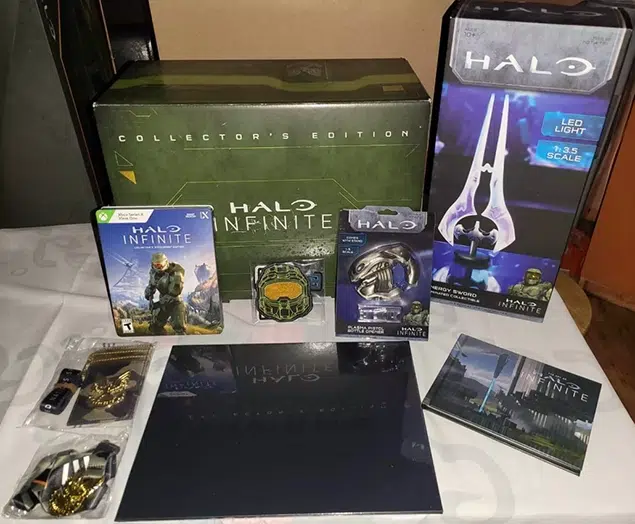
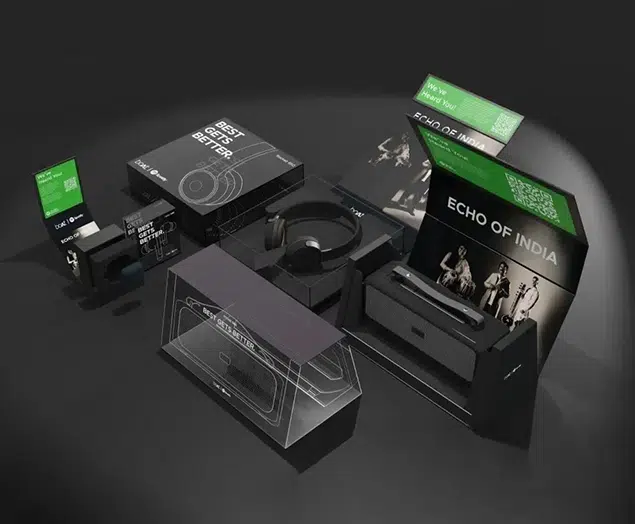
Unlike primary packaging, secondary packaging refers to the outer layer that contains and protects multiple units of primary packaged products. It plays a critical role in logistics, transportation, and shelf display. Secondary packaging is often referred to as the “retail packaging” and includes items such as cardboard boxes, cartons, trays, or shrink wrap. The functions of secondary packaging are as follows:
- Bulk Packaging and Unitization: Secondary packaging facilitates efficient handling, shipping, and storage of multiple units of primary packaged products. It enables unitization, allowing easier counting, grouping, and inventory management.
- Protection During Transit: Secondary packaging provides an additional layer of protection to primary packaged products during distribution, minimizing the risk of damage, breakage, or contamination.
- Shelf-Ready Presentation: Secondary packaging is designed to enhance product visibility, organization, and attractiveness on retail shelves. It includes attention-grabbing graphics, branding elements, and display features to capture consumers’ attention and drive sales.
- Brand Cohesion: Secondary packaging ensures a cohesive brand experience across various products in a line or product range. It may bear consistent branding elements or designs that align with the primary packaging to reinforce brand recognition and build brand loyalty.
Primary Packaging Versus Secondary Packaging
In the world of packaging, primary and secondary packaging form a cohesive system that combines both product protection and market appeal. Primary packaging engages consumers directly, encapsulating the individual product and representing the look and feel of the brand. On the other hand, secondary packaging offers logistical support, providing protection during transit and promoting products on retail shelves.
By understanding the roles and functions of primary and secondary packaging, businesses can create a comprehensive packaging strategy that effectively showcases their products, protects them throughout their journey, and leaves a lasting impression on consumers. Successful packaging considers both the practical aspects of product protection and the emotional connection it creates with consumers. Achieving a harmonious balance between primary and secondary packaging is key to delivering a remarkable product experience from shelf to consumer’s hands.
Both primary and secondary packaging are essential components of successful product packaging. The choice between the two depends on factors such as product type, industry, distribution channel, branding strategy, and cost considerations. Primary packaging focuses on direct product protection, usability, and branding, while secondary packaging excels in logistical support, retail presentation, and sustainability. The optimal approach is to strike a balance between these two types of packaging, ensuring that products are well-protected, visually appealing, and efficiently transported while aligning with brand values and meeting consumer expectations.


Top 10 Creative Cosmetic Packaging Design Ideas & illustrations 2023 | Luxury-Paper-Box.Com

Perfume Packaging Design Trends 2025

Best Chocolate Packaging Designs of 2025

How E-commerce Packaging Wins Hearts (and Wallets)


 kali@luxury-paper-box.com
kali@luxury-paper-box.com